Category: Event
Is Your Home Ready for Extreme Weather?
January 1, 2025
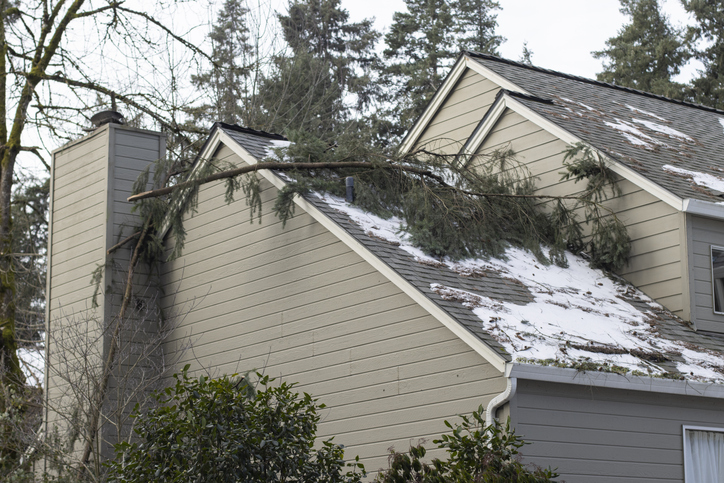

From wildfire season with smoky air to higher temperatures and unexpected blackouts during freezing temps, the reality of extreme weather conditions is causing homeowners to better prepare their homes. While every homeowner should feel safe at home, a recent survey by Certain Teed revealed that less than 48% of people feel confident in their home’s durability in the face of extreme weather.
The good news is that smart updates will bring peace of mind and add value to your home. While some projects cost more money and time than others, there are several that require less of an upfront investment. No matter your budget, here are five easy home improvement areas to consider to protect your home and feel safer during weather events.
HVAC Systems Can Protect Against Temperatures and Poor Air Quality
Because people spend 90 percent of their time indoors, the quality of your home’s indoor air is crucial to the quality of your home life. One way homeowners can prepare for extreme weather and climate events is to make sure they have a reliable and well-maintained HVAC system in place. While it can be difficult to predict when climate-related issues may happen, an HVAC system can maintain inside temperatures, withstand harsh weather outside, and provide filtration that improves indoor air quality no matter what unfolds.
Preventative maintenance on your HVAC system and changing the filter every 30 to 90 days will help prolong the life and quality of your investment. Keeping your system at or above 64 degrees Fahrenheit during the colder months also helps prevent expensive issues like frozen and burst pipes.
Choose the Right Roofing Materials For Your Climate
Roof upgrades significantly increase your home’s resilience as well as its value. “The roof is the first line of defense on a home,” says Teed Lucas Hamilton, manager of applied building science at Certain. “It is important to select the right materials for your climate,” he says. Impact-resistant roofing, solar reflective shingles to combat rising temperatures, and fire-resistant materials are all things to consider when choosing roofing materials. In areas where strong wind is a possibility, hurricane fastening and straps can also further secure your roof.
When updating the roof, take into account the gutters. Simple add-ons like leaf filters help prevent blockages so that water doesn’t back up during heavy rainfall. When flooding is a concern, gutters should direct drainage away from the home’s foundation. Too much water around the foundation can lead to serious structural issues in the future, such as cracks in the foundation. A sump pump, which runs automatically to keep water out of basements and away from the foundation, is another wise investment in areas with heavy rain and storms.
Consider Window Updates or Replacements
In areas where debris impact is an issue, shutters that can cover existing windows ahead of a storm can safeguard a home during large storms. Impact windows, which have a heavy-duty frame and glass that’s engineered to remain intact even if it breaks in a collision, are another option, but depending on the number of windows your home has, they can get expensive.
Less expensive alternatives to shutters and window replacements include sealing existing windows and applying tints.
“First, use caulk to seal up any holes and cracks on the outside. Then apply weatherstripping and use a window or door insulation kit to block the cold and heat from the inside,” Hamilton says. “These changes help strengthen the barrier between your home and the outdoors, saving on heating and cooling and keeping the elements outside.”
Applying window tinting is another example of an inexpensive update that can block up to 80% of summer solar heat while also keeping some heat inside during winter months. Updates such as these protect from weather and increase energy efficiency by creating a better barrier between your home and the outside elements.
Make Simple Exterior Updates
Steel doors, which are made of more durable materials than some more elaborate door styles, upgrade a home’s entry points by withstanding storms. When certain updates, such as replacing every window in the house, are not in your budget, replacing the home’s main entry points with stronger doors can be a good place to start.
Changing the color of your exterior paint is another affordable update that can help with temperature control. “You might think that choosing the exterior color of your home is only about picking what color you like best,” says Angie Hicks, co-founder of Angi, formerly known as Angie’s List. “The climate you live in is crucial to picking the right color.”
In hot climates, light colors will help to reflect the sun and keep the interior cool, while those who live in climates prone to extreme colds should choose darker tones to retain heat better.
Maintenance is Key to Safeguarding Your Property
With increased extreme weather events, your home could be damaged slowly over time. It becomes more important to inspect your home for changes and keep up on maintenance to prevent larger repairs and damage down the road. Checking your roof after storms, such as noting any cracks, sagging, or debris in the gutters, is an important part of keeping your roof resilient during the next event. Trees around your home should also be checked for cracks in large branches or soggy soil around the roots, as those should be addressed to prevent damage in a future storm. Gutters should also be cleared regularly to prevent blockages, as well as collect debris from the yard that could become projectiles.
Insureyouknow.org Make sure you’re aware of how your community issues weather alerts. While some use outdoor sirens, others depend on media and smartphones to alert residents of severe storms. No matter what kind of hazards your community may be prone to, the National Weather Service recommends developing a plan with your family ahead of time, such as knowing where your emergency meeting place is or where the safe room is in your home. Safe rooms are usually those without windows at the lowest level of your home. In the event that your home is compromised, Insureyouknow.org can protect all of your vulnerable paper documents by ensuring digital access, providing you with one less thing to worry about so that you may focus on the safety of yourself and your loved ones.
Preparing for a Flood Before Disaster Strikes
October 15, 2022
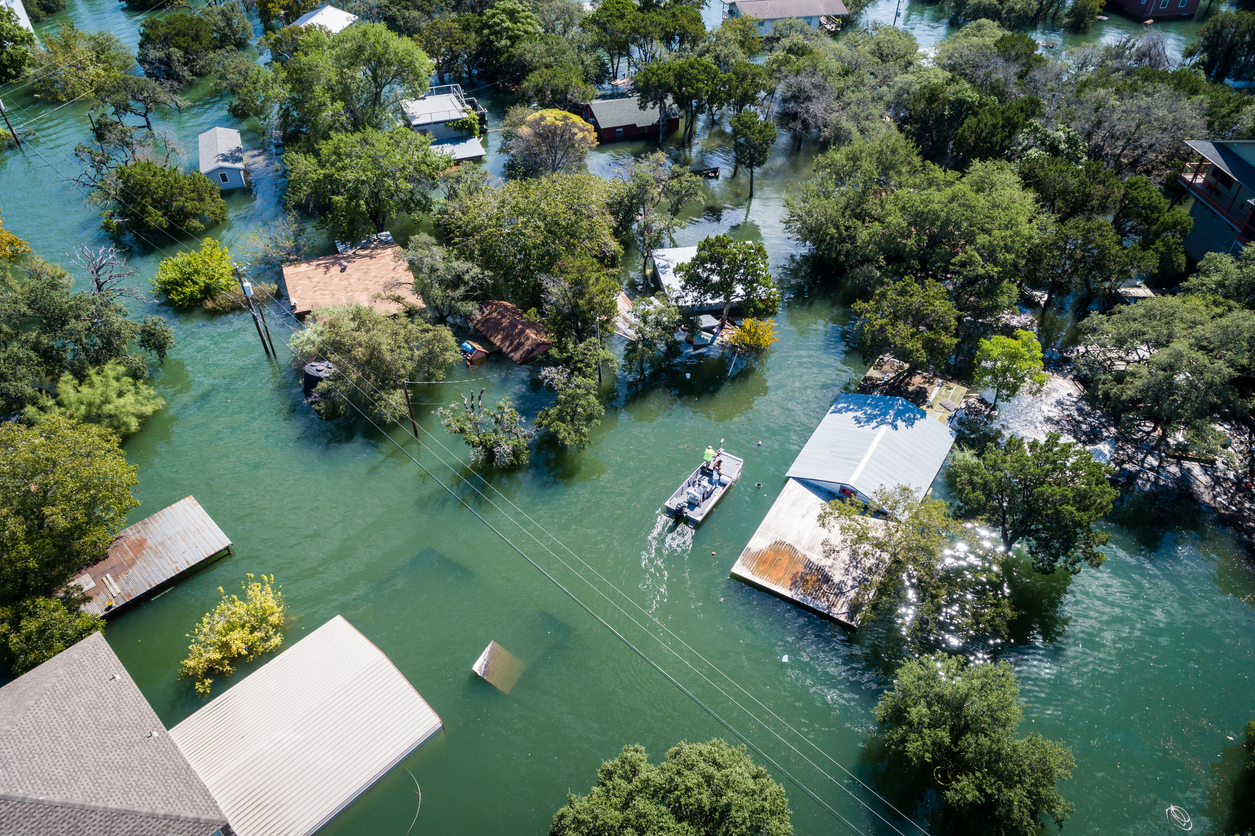

Flooding is the most common and most damaging natural disaster in the country. In Florida, where Hurricane Ian’s floodwaters turned towns into rivers, flood risk is higher due to the state’s frequency of storms and proximity to water. Despite this, most insurance policies do not automatically cover flooding. No matter where you live, you should check your auto and homeowner’s or renter’s insurance policies as an initial step in preparing for a flood to keep you and your loved ones safe when a flood interrupts your lives.
Determining Your Risk Level
To find out the risk level of your property location, visit FloodSmart.gov/Flood-Map-Zone.
Because research has found that FEMA’s flood maps underestimate the danger in some areas as climate change advances, homeowners and renters unaware of their level of risk should act on the following points:
- Are you in a flash-flood-prone area? Contact the local county geologist or county planning department to find out if your home is in a flash-flood-prone area or a landslide-prone area.
- Make a communication plan and a disaster plan for your family.
- Plan and practice a flood evacuation route with your family. Ask an out-of-state relative or friend to be the “family contact” in case your family is separated during a flood. Make sure everyone in your family knows the name, address, and phone number of your contact person.
- Stay informed. Learn about your community’s emergency plans, warning signals, evacuation routes, and locations of emergency shelters.
- Inform local authorities about any special needs, such as elderly or bedridden people, or anyone with a disability.
Preparing Your Home for a Flood
- Make sure you secure or protect any hazards in your home before the flood strikes.
- Be prepared to turn off electrical power when there is standing water, fallen power lines, or before you evacuate. Turn off gas and water supplies before you evacuate. Secure structurally unstable building materials.
- Buy a fire extinguisher if you don’t already have one. Make sure your family knows where it is and how to use it.
- Buy and install sump pumps with backup power.
- Have a licensed electrician raise electric components (switches, sockets, circuit breakers, and wiring) at least 12″ above your home’s projected flood elevation.
- For drains, toilets, and other sewer connections, install backflow valves or plugs to prevent floodwaters from entering.
- Anchor fuel tanks can contaminate your basement if torn free. An unanchored tank outside can be swept downstream and damage other houses.
Creating an Emergency Supply Kit
Stock your home with supplies you may need during the flood by creating an emergency supply kit. Visit the CDC’s Personal Health Preparedness page for a list of supplies you’ll want to include in your kit.
Preparing Food and Water Supplies
Make sure you and your family have enough safe food and water (for drinking, cooking, and bathing) available in the event of a flood. For more information, visit Food and Water Needs: Preparing for a Disaster or Emergency.
Reentering Your Flooded Home
When returning to a home that’s been flooded after natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods, be aware that your house may be contaminated with mold or sewage, which can cause health risks for your family. See the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s guidelines for reentering your flooded home.
Reviewing Flood Insurance Options
Although you can purchase flood insurance at any time, waiting until a hurricane or major storm is threatening your home may be too late. Many policies take at least 30 days after purchase to take effect.
The National Flood Insurance Program is a pre-disaster flood mitigation and insurance protection program designed to reduce the escalating cost of disasters. This program makes federally backed flood insurance available to residents and business owners. Standard flood insurance by the National Flood Insurance Program generally covers physical damages directly caused by flooding within the limits of the coverage purchased. Private providers may have higher limits or broader coverage compared to National Flood Insurance Program policies.
Regardless of which policy you select for your business or family, any coverage is better than none. If your property experiences flooding impacts from a disaster, it is not guaranteed you will be able to receive federal assistance. If your area has not received a Presidential Disaster Declaration that makes federal assistance available under FEMA, you will not receive federal assistance.
When there is an official Presidential Disaster Declaration, National Flood Insurance Program policyholders are encouraged to apply for FEMA disaster assistance in addition to their flood insurance claim. For more information, visit National Flood Insurance Program or call1-800-621-FEMA.
Filing a Flood Insurance Claim
Flood insurance claims can be filed anytime you experience flooding on your property and can cover both a property and its contents.
If you need to file a flood insurance claim, be informed and prepared so that recovery can move quickly and smoothly. Before a disaster strikes, have updated photos of your home or business so that insurance providers can clearly examine your property and belongings. If your property has experienced flood impacts, take extensive photos of the damages before cleaning up. This will allow insurance providers to compare before and after photos to determine the extent of damages and arrange the best claim payment possible. As you’re cleaning, make a detailed list of lost or damaged items. If you have original receipts for items, hold onto those for documentation in your claim. After gathering all the necessary information, contact your insurance company to begin filing your claim.
InsureYouKnow.org
At InsureYouKnow.org, file your auto, and homeowner’s or renter’s insurance policies, photos before and showing flood damage, an inventory of your home and possessions, and your checklists of supplies needed for emergency events. If you are impacted by a flood, also keep track on this portal of your insurance claims and interactions with your insurance company and FEMA.
College Graduates’ Guide to Insurance
May 31, 2022

Congratulations to college graduates everywhere as the graduation season kicks off in 2022! Homework continues, however, as grads meet the challenges presented by their next decisions—changing their residences, jobs, and insurance coverages. Even though this last item may not be as exciting as finding a new place to live or pursuing a lucrative career opportunity, the following options in insurance coverages are important issues that new college grads need to address.
Health Insurance
Since the passage of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), choosing new coverage—or holding on to existing coverage—has been much easier for college graduates who may decide to:
1. Remain on a parent’s insurance plan
Before the ACA was enacted, it was common for health insurance plans to drop dependents as soon as they graduated from college. But the ACA requires almost all health plans that offer dependent coverage to allow young adults to remain on a parent’s plan until they turn 26. So, for young adults covered under a parent’s plan, graduating from college no longer requires them to quickly find new health insurance.
2. Purchase a short-term plan
Short-term health insurance is a potential alternative for college grads who need temporary coverage to tide them over until another policy kicks in. Even for grads who have a job lined up right away, employers often have a waiting period before health insurance coverage is available to new hires. Short-term plans can be purchased at any time of the year, with immediate effective dates available.
3. Buy an ACA-compliant individual plan
For new grads who want a more robust, ACA-compliant plan that covers the essential health benefits and pre-existing conditions, a plan purchased through the state health insurance exchange is likely to be an ideal solution. For more information about marketplace insurance, visit www.healthcare.gov.
4. Check Medicaid eligibility
In 38 states, Medicaid has been expanded to cover all adults with income up to 138 percent of the poverty level. In 2022, that’s $18,754 for a single individual, except in Alaska and Hawaii where the limit is higher. Medicaid enrollment is available year-round and coverage includes pre-existing conditions. In most cases, there are no premiums. For a new grad living in a state where Medicaid has been expanded, this could be a perfect solution during the weeks or months that it might take to find a job after graduation.
5. Get coverage through a new employer
College grads may be able to enroll in group coverage at their new jobs. Employer-sponsored health insurance generally offers substantial benefits, and employers typically pay a large portion of the premiums. Employee contributions are paid through payroll deductions. Participants also may be eligible to enroll in a Health Savings Account that minimizes the financial impact of out-of-pocket medical expenses.
Renters’ and Homeowners’ Insurance Policies
Before graduation, college students probably lived in a dorm room or shared housing with other students. Now, it may be time for them to relocate to their first apartment, condo, or house.
Renters need to understand that their landlord’s insurance doesn’t cover their belongings. Suppose renters experience an unforeseen situation, including burglary, stormy weather that causes a leaky roof to destroy their furnishings, or a fire that creates smoke damage. In these scenarios, they could be protected by renters’ insurance.
Homeowners’ insurance policies, available to college grads buying their first condos or houses, combine several types of coverage, including dwelling, personal property, other structures, loss of use, personal liability, and medical payments into one policy,
It’s a good idea for renters and homebuyers to create a spreadsheet with an inventory of the contents of their residences, placing approximate values on their belongings.
Auto Insurance
Upon completing college, grads may be ready to buy a new car that requires upgrading their auto insurance, especially if they had been previously covered under their parents’ policy. Personal auto insurance is a package policy providing four coverages—liability, medical payments, uninsured and underinsured motorist, and physical damage.
Life Insurance
Unless a college grad is married or has individuals, such as a child or an aging parent dependent on their income, life insurance may not be needed right away. However, if young adults are single, healthy, and in a family with a good health history, they may be at an insurability peak and would benefit from the best rates on life insurance.
InsureYouKnow.org
College graduation prompts a transition from a school-based existence to one replete with adult responsibilities, including the need to put insurance policies in place. By preparing for the unforeseen future, college grads who do their homework on insurance options and keep copies of policies, inventories of their belongings, and records of any claims submitted at insureyouknow.org, can begin living their lives to the fullest.
Steps to Take in American Heart Month
February 15, 2022

February, celebrated as American Heart Month, is a time to reflect on your heart health, consider your risk factors, and take steps toward preventing heart disease and stroke.
Review these seven signs for heart disease risk:
- Smoking. More than 35 million adults in America are smokers, and thousands of young people pick up the habit daily. If you don’t smoke, don’t start. If you’re a smoker, do your best to quit or cut down. The American Lung Association can help tobacco users figure out their reasons for quitting and then take the big step of quitting for good.
- Physical inactivity. Regular physical activity helps improve overall health and reduces the risk for heart disease, stroke, and premature death. In people with cardiovascular disease, physical activity can help manage their conditions; exercise training has been shown to have a positive effect on people with certain types of heart failure, and cardiac rehabilitation, which includes physical activity training, helps improve the health of people who have had a heart attack or bypass surgery.
- Nutrition. Make heart-healthy diet decisions. Eat whole foods low in trans-fat, saturated fat, sodium, and added sugar. Nutritionists recommend that you fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables.
- Overweight/Obesity. People overweight or obese have a higher risk for heart disease. Carrying extra weight can put extra stress on the heart and blood vessels. To find out if your weight is in a healthy range, you can calculate your Body Mass Index (BMI) at CDC’s Assessing Your Weight website.
- High Cholesterol. Your health care team should test your blood levels of cholesterol at least once every 4 to 6 years. If you have already been diagnosed with high cholesterol or have a family history of the condition, you may need to have your cholesterol checked more often. Talk with your health care provider about this simple blood test. If you have high cholesterol, medicines and lifestyle changes can help reduce your risk for heart disease.
- Diabetes. If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels carefully. Talk with your health care team about treatment options. Your doctor may recommend certain lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar under control. These actions will help reduce your risk for heart disease.
- High Blood Pressure. Millions of people in the United States have high blood pressure, and millions of them are as young as 40 or 50. If you are one of them, talk to your doctor about ways to control it. High blood pressure usually has no symptoms, so have it checked on a regular basis. Your health care team should measure your blood pressure at least once every 2 years if you have never had high blood pressure or other risk factors for heart disease.
If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also called hypertension, your healthcare provider will measure your blood pressure more often to make sure you have the condition under control. Ask how often you should check your blood pressure which can be done at a doctor’s office, at a pharmacy, or at home.
Your health care team might recommend some changes in your lifestyle, such as lowering sodium in your diet; your doctor also may prescribe medicine to help lower your blood pressure.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many people have put off scheduling a routine annual physical examination. Healthcare professionals take precautions daily to prevent the transmission of COVID-19 in their facilities. If you feel comfortable with your vaccination status and safety measures in place, make an appointment to find out if you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol and to address other risk factors.
InsureYouKnow.org
After you check in with your healthcare provider to rate your risk for heart disease and stroke, keep track of recommended prevention steps, prescribed medications, lab test results, and a calendar of completed and upcoming appointments at insureyouknow.org.
The Great Resignation Continues in 2022
January 29, 2022
“The Great Resignation” is a term coined in May 2021 by Anthony Klotz, Ph.D., an associate professor of management at Mays Business School at Texas A&M University who predicted the mass exodus of employees abandoning jobs during the pandemic.
In April, a month before Dr. Klotz made this prediction, a record 4 million people quit their jobs, many of them in low-paying, inflexible industries such as retail trade sectors and food services. He explained that during the pandemic, employees have been able to reflect about family time, remote work, commuting, passion projects, life and death, and what it all means which led workers to consider alternatives to their current positions.
Because the latest data suggests this trend, also called the “Big Quit,” will continue through 2022, employees, as well as employers, must prepare for changes in the workforce.
Employees
Before you submit your resignation, consider the following suggestions to guide your decision:
- Reassess your duties: Expanding your responsibilities within the company may offer the growth that you’re looking for without leaving your workplace. Promotion within your company may lead to a higher salary and additional benefits. On the other hand, you may feel overworked or are experiencing burnout, resulting in work-related stress, and seeking a less demanding opportunity may be a solution during this difficult time.
- Meet with your employer: If you prefer to work remotely, meet with your employer and plead your case to work all or part of your workweek away from the corporate office, especially if you have health and safety concerns, childcare issues, or COVID-related care responsibilities. Explain how important work/life flexibility is to you and ask if your employer is willing to consider your needs for your home life situation. Take this opportunity to ask if your salary, benefits, and health insurance could be improved to entice you to stay.
- Be flexible with your transition: If possible, notify your supervisor in person when you decide to resign and be flexible about the ending date in your position. Be professional in your exit interview, request a letter of recommendation for your files, find out when you’ll receive your last paycheck, and ask about the continuation of your benefits.
- Assess your financial situation: If you determine that you need to continue receiving a steady paycheck and insurance benefits, secure another position or outline a solid self-employment opportunity before you resign. If you are close to retirement age, figure out if you can delay collecting Social Security and retirement benefits so you can collect higher monthly payments in the future.
Employers
Employers who want to reduce staff turnover and retain experienced employers may benefit from the following tips adapted from the article, “How Employers Can Overcome The Great Resignation” from the Worth Media website.
- Be creative in putting together benefits packages that can support a diverse workforce with broad, varying needs.
- Remain flexible when employees choose their work locations.
- Keep an open line of communication with your employees.
- Emphasize the importance of employees’ mental and physical well-being.
- Prioritize pay equity and adopt a spirit of transparency.
- Remind your employees about your company’s mission, values, and vision.
- Treat employees who do leave with respect, a sense of professionalism, and kindness.
Employers’ main goal during this tumultuous time should be to remain calm, listen to employee feedback, and use it to make any necessary changes to their business model, benefits package, and salaries.
InsureYouKnow.org
Are you planning to join “The Great Resignation” in 2022? If so, consider not only how you can improve your present work situation but also what the future may hold for your career choices, continuing education, home life, insurance coverage, and financial goals. As you put each of these options in place, keep records regarding your decisions at insureyouknow.org.
Track Your Gifts on a Home Inventory
December 14, 2021

Lucky you! You’ve been nice, not naughty, so, you may be rewarded with gifts galore this holiday season. What’s on your wish list—a smart TV, a laptop computer, or a sporty new vehicle? In all the excitement of opening and enjoying your generous bounty, remember to keep track of your new acquisitions by adding them to your home inventory. If you’ve never compiled a home inventory, you can start with recent gifts and then add older possessions. You’ll also want to update your home inventory regularly and add new items or delete possessions you no longer own.
Why Should You Maintain a Home Inventory?
In the event of a burglary, fire, or another disaster, if you have an up-to-date home inventory, you’ll be able to file a detailed insurance claim quickly, settle faster, and receive compensation promptly. You also should review the current value of items you own in case you need to increase your home insurance coverage.
What Should You Include in a Home Inventory?
- A description of each item you possess, including the make, model, and serial number
- The estimated value of the item/replacement cost
- Appraisal or cost at the time of purchase
- Purchase date
- Receipt and source of purchase
- Photos of each item taken with your cell phone or digital camera
- Detailed description about the item if received as a gift
How Do You Make a List?
Here are some suggestions to help you organize your list:
- By room. Choose a room and list all the contents. For example, start in your living room and list everything, like your TV, sofa, recliner, and side tables. Remember to list even the mall stuff, like books, knickknacks, and decorations on your shelves.
- By groups of items. Or group together items like antiques, artwork, clothes, collections, jewelry, kitchen items, furniture, musical instruments, and miscellaneous items.
- Off-site items. Make sure you include belongings you keep in a self-storage unit covered by your homeowner’s insurance.
Although you may be faced with the daunting challenge to document all your possessions in compiling a home inventory, persevere even if you can’t get it all done immediately. It’s better to have an incomplete inventory than not to have any assets recorded.
Should You Reevaluate Your Insurance Coverage?
While you’re documenting all your possessions, look at high-value items such as jewelry, musical instruments, artwork, camera equipment, and electronics. Keep in mind that your homeowner’s insurance might put a special sublimit on certain types of items. Realize that just because you have an item on your home inventory list, doesn’t mean you will get paid for it. Check your policy’s declaration page for special limits for specific categories of merchandise. You may need to purchase an insurance rider for items such as jewelry and specialized collections.
For example, a common homeowner’s insurance policy puts a $1,500 limit on theft coverage for jewelry and watches. If you have valuable items, you can “schedule” them. Scheduled personal property is an add-on to homeowners’ or renters’ insurance to insure high-value items for their full value.
Make sure your policy covers the replacement value of your possessions, not the actual cash value. An actual cash value payment would pay you only the depreciated value of your items, not new replacements.
If you live in an area that’s prone to earthquakes or floods, you could consider earthquake insurance or flood insurance. Without them, your home and belongings won’t be covered in certain disaster situations.
InsureYouKnow.org
After you have created a detailed home inventory, you can store it at insureyouknow.org. You’ll be able to access your list of possessions and add, delete, or refine entries regularly. With a current record of your newly acquired and older possessions on file, you’ll be prepared if you need to file an insurance claim or reevaluate your insurance coverage.
The Most Wonderful/Stressful Time of the Year
December 1, 2021

Welcome to what is referred to as both the “most wonderful” and the “most stressful time of the year.” During the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic, you may be experiencing stress and depression—unwanted emotions that can ruin your holidays and impact your physical and mental health.
Although you can’t control inflation, high gas prices, food and toy shortages, and shipping delays, you can be realistic, plan ahead, and seek support to overcome holiday stress and depression. You may even end up embracing the “most wonderful time of the year.”
Tips to Deal with Seasonal Pressures
Be realistic. COVID-19 cases are on the rise in some areas and even if you’ve been vaccinated, you may decide not to gather with friends and relatives in person. You can opt for a virtual celebration or increase efforts to share photos, texts, emails, phone calls, or videos with loved ones.
Avoid overspending, especially if you’re already feeling financial stress. Consider alternatives to expensive gifts by donating to charities in giftees’ names or by making and giving homemade presents.
Strive to decorate your home, create meals and desserts, and select gifts that will be appreciated not because they are “perfect” but because they are heartfelt and sincere.
Plan ahead. Compile lists of recipients and specific gift ideas; don’t go to browse in busy stores, hoping for inspiration. Save time and frustration caused by traffic and parking congestion by shopping online for items on your gift list. Schedule specific times to shop, bake, and attend social events. Plan menus and then create a detailed grocery list to prevent forgetting needed ingredients.
Acknowledge your feelings. Stress about gatherings with family and friends, or feeling grief about missing loved ones, may result in sadness and grief. Take time to acknowledge and express your feelings. You can’t force yourself to be happy just because it’s the holiday season. If you celebrate in person or in other ways as described above, set aside differences and controversial topics and concentrate on positive conversations.
Practice mindfulness by bringing your attention to the present moment and avoid getting stressed about past or future events.
Reach out. If you feel lonely or isolated, seek out community, religious or other social events, or communities. Many helpful organizations have websites, online support groups, social media sites, or virtual events that can offer support and companionship.
Volunteering your time and doing something to help others also are good ways to lift your spirits and broaden your friendships. Consider dropping off a meal and dessert at a friend’s home or to a community center that serves less fortunate individuals during the holidays.
Learn to say no. Set priorities based on preserving your well-being and don’t overextend yourself or you may wind up feeling resentful and overwhelmed. Learn to feel guilt-free when you decline invitations and recognize that you sometimes need to allow yourself to say no to demands on your time.
Maintain healthy habits. Get ample sleep, eat well—even at holiday events—and stay physically active in your daily routine. Maintaining healthy habits during the holiday season will be one of your best defenses against stress. When you feel a bout of stress coming on, have a healthy snack before a holiday party to curb your desire for high-calorie food and drink. Try deep-breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. Avoid excessive tobacco, alcohol, and drug use.
Take a breather. Make time for yourself. Find an activity you enjoy like taking a walk, listening to calming music, or reading (or listening to) a book. Disconnect temporarily from social media and electronic devices.
Seek professional help if you need it. Even after following all the tips listed above, you may find yourself feeling continuously sad or anxious, beset by physical complaints and lack of sleep, and unable to face daily chores. If these feelings last for a while, talk to your doctor or a mental health professional. If you rely on medications to maintain your physical and mental health, make sure your prescriptions are up-to-date and that you have an adequate supply when your doctor’s office or pharmacy may be closed or have reduced hours during the holidays.
InsureYouKnow.org
At InsureYouKnow.org, you can keep a handy record of your prescriptions, refill expiration dates, and contact information for healthcare providers who prescribe and pharmacies that fill your medications.
Death (of a Spouse) and Taxes
November 16, 2021

In a “normal” year, about 1.5 million Americans become widows and widowers, but the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly increased that annual statistic. According to a recent article in The Wall Street Journal, the National Center for Family and Marriage Research at Bowling Green State University estimates that about 380,000 of the more than 700,000 people in the United States who have died from COVID-19 were married.
Under “normal” circumstances, it may be difficult to comply with tax requirements and deadlines; filing as a widow(er) presents additional challenges. This is a complex topic with the following issues to consider.
Filing the First Year
The IRS stipulates that the year that your spouse dies:
- You can still file a joint return if you didn’t remarry and the executor approves the joint return.
- If either spouse was a nonresident alien at any time during the year, the surviving spouse can’t file a joint return.
- If you do file jointly, include all your income and deductions for the full year, but only your spouse’s income and deductions until the date of death.
- If the deceased spouse owes any taxes that the estate can’t pay, you as the surviving spouse may be liable for the amounts owed.
Filing in the Next Two Years
For two tax years after the year your spouse died, you can file as a qualifying widow(er). This filing status gives you a higher standard deduction and lower tax rate than filing as a single person. You must meet these requirements:
- You haven’t remarried.
- You must have a dependent (not a foster) child who lived with you all year, and you must have paid more than half the maintenance costs of your home.
- You must have been able to file jointly in the year of your spouse’s death, even if you didn’t.
Notifying the IRS
If you are a widow(er) who
qualifies to file a joint return, take the following steps:
- Across the top of your IRS Form 1040 tax return for the year of death—above the area where you enter your address, write “Deceased,” your spouse’s name, and the date of death.
- When you’re a surviving spouse filing a joint return and a personal representative hasn’t been appointed, you should sign the return and write “filing as surviving spouse” in the signature area below your signature.
- When you’re a surviving spouse filing a joint return and a personal representative has been appointed, you and the personal representative should sign the return.
- A decedent taxpayer’s tax return can be filed electronically. Follow the specific directions provided by your preparation software for proper signature and notation requirements.
- The deadline to file a final return is the tax filing deadline of the year following the taxpayer’s death.
- If you are a surviving spouse filing a joint return alone, you should sign the return and write “filing as surviving spouse” in the space for your deceased spouse’s signature.
- If a refund is due, there’s one more step. You also should complete and file with the final return a copy of Form 1310, Statement of Person Claiming Refund Due a Deceased Taxpayer. Although the IRS says you don’t have to file Form 1310 if you are a surviving spouse filing a joint return, you probably should file the form to prevent possible delays.
Other forms and documents you may need include:
- W-2s, 1099s and other tax forms for the year of death, reporting income or expenses paid before the person died.
- Death certificate to prove the date of death in the tax year being reported.
- Form 56 filed by a trustee, executor, administrator, or other person to let the IRS know who is responsible for the person’s estate.
- Form 1041, “U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts” reports receipt of more than $600 in annual gross income (such as dividends, interest, proceeds from the sale of assets) after the person died.
- IRS Publication 559, “Survivors, Executors and Administrators” provides more information about legal requirements.
Note: You can’t file a final joint return with your deceased spouse if you as the surviving spouse remarried before the end of the year of death. The filing status of the decedent in this instance is married filing separately.
Filing an Estate-tax Return
The current estate- and gift-tax exemption is $11.7 million per individual, so not many estates owe tax—only about 1,900 did for 2020, according to the Tax Policy Center. Executors don’t need to file a return if the decedent’s estate is below the exemption.
They may want to file one, however, because then the surviving spouse can have the partner’s unused exemption and add it to their own in many cases.
Estate taxes are normally due nine months after the date of death. But the IRS allows executors to claim the unused exemption for the spouse up to two years after the date of death, in many cases.
Selling a Home and Resulting Exemptions
Survivors who sell a home may take up to $500,000 of home-sale profit tax-free if they haven’t remarried and sell within two years of the partner’s date of death. If they sell later, the exemption drops to $250,000, the standard amount for single filers.
Dealing with Retirement Accounts
Surviving spouses can roll over inherited retirement accounts such as 401(k)s and IRAs into their own names, and financial advisers routinely recommend this move.
A new widow(er) should carefully consider options. It’s possible to divide retirement accounts such as IRAs, and to roll over some but not all assets into the survivor’s name. This would leave the remainder in an inherited IRA available for penalty-free payouts to younger spouses.
Either way, heirs of retirement accounts should be sure to name new heirs of their own.
Heirs of these accounts who will face higher taxes as single filers may also want to convert assets to Roth IRAs, which can have tax-free withdrawals—especially if they can convert while still eligible for joint-filing rates and brackets.
Cashing U.S. Savings Bonds
There’s a special rule for U.S. Savings Bonds, from which income generally accrues tax-free until the bonds are cashed in. When the bond owner dies, the accrued interest may be treated as income in respect of a decedent.
In that case, the new owner of the bonds becomes responsible for the tax on the interest accrued during the life of the decedent. (The tax isn’t due, however, until the new owner cashes in the bonds.)
Alternatively, the interest accrued up to the date of death can be reported on the decedent’s final income tax return. That could be a tax-saving choice if he or she is in a lower tax bracket than the beneficiary. If that method is chosen, the person who gets the bonds only includes in income the interest earned after the date of death.
Reporting Deductions
All deductible expenses paid before death can be written off on the final return. In addition, medical bills paid within one year after death may be treated as having been paid by the decedent at the time the expenses were incurred. That means the cost of a final illness can be deducted on the final return even if the bills were not paid until after death.
If deductions are not itemized on the final return, the full standard deduction may be claimed, regardless of when during the year the taxpayer died. Even if the death occurred on January 1, the full standard deduction is available.
Inheriting Property and Money
For deaths that occurred in years other than 2010, the tax basis of any property a taxpayer owns at the time of his or her death is “stepped up” to its date-of-death value. Since the basis is the amount from which any gain or loss will be figured when the new owner ultimately sells the property, this means that the tax on any appreciation that occurred during the taxpayer’s life is essentially forgiven.
The person who inherits the property—a house, say, or stocks and bonds— would owe tax only on appreciation after the time of death. It’s important that you pinpoint date-of-death value as soon as possible—the executor should be able to help—to avoid hassles later on when you sell it. If assets have lost value during the original owner’s life, the tax basis is stepped down to date-of-death value.
Money you inherit is generally not subject to federal income tax. If you inherit a $100,000 certificate of deposit, for example, the $100,000 is not taxable. Only interest on it from the time you become the owner is taxed. If you receive interest that accrued but was not paid prior to the owner’s death, however, it is considered income in respect of a decedent and is taxable on your return.
InsureYouKnow.org
The death of a spouse not only presents emotional distress resulting from the loss of a loved one, but it also forces a widow(er) to deal with income tax issues never before faced. By keeping at insureyouknow.org, copies of a spouse’s death certificate, medical bills, income records, property assessments, and wills, you’ll be able to access required documents when you file your income tax return following the death of a spouse.
August = Back to School
July 30, 2021

Back to School Month has been observed in August since the 1960s to help parents, students, and teachers prepare for a new academic year. In addition to shopping for back-to-school supplies, backpacks, and clothes during the month, parents also will need to address how the coming academic year could look different, especially if their children attended virtual classes exclusively during the 2020-2021 school year.
In reaction to the COVID-19 pandemic, physical arrangements in schools could result in the placement of desks far apart from one another, maintenance of physical distance by teachers and students, the possibility of students and teachers staying in their classrooms for lunch, and the wearing of face masks.
COVID-19 also can affect children and young people socially, emotionally, and mentally. These issues also need to be addressed when students return in person to school.
COVID-19 Prevention in Schools
To help students return to school in person, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides Guidance for COVID-19 Prevention in K-12 Schools, that includes the following key takeaways.
- Students benefit from in-person learning, and safely returning to in-person instruction in the fall 2021 is a priority.
- Vaccination is currently the leading public health prevention strategy to end the COVID-19 pandemic. Promoting vaccination can help schools safely return to in-person learning as well as extracurricular activities and sports.
- Masks should be worn indoors by all individuals (age 2 and older) who are not fully vaccinated. Consistent and correct mask use by people who are not fully vaccinated is especially important indoors and in crowded settings, when physical distancing cannot be maintained.
- CDC recommends schools maintain at least 3 feet of physical distance between students within classrooms, combined with indoor mask wearing by people who are not fully vaccinated, to reduce transmission risk. When it is not possible to maintain a physical distance of at least 3 feet, such as when schools cannot fully re-open while maintaining these distances, it is especially important to layer multiple other prevention strategies, such as indoor masking.
- Screening testing, ventilation, handwashing, and respiratory etiquette, staying home when sick and getting tested, contact tracing in combination with quarantine and isolation, and cleaning and disinfection are also important layers of prevention to keep schools safe.
- Students, teachers, and staff should stay home when they have signs of any infectious illness and be referred to their healthcare provider for testing and care.
- Many schools serve children under the age of 12 who are not currently eligible for vaccination. Therefore, this guidance emphasizes implementing layered prevention strategies to protect people who are not fully vaccinated, including students, teachers, staff, and other members of their households.
- COVID-19 prevention strategies remain critical to protect people, including students, teachers, and staff, who are not fully vaccinated, especially in areas of moderate-to-high community transmission levels.
- Localities should monitor community transmission, vaccination coverage, screening testing, and occurrence of outbreaks to guide decisions on the level of layered prevention strategies.
COVID-19 Stress and Coping
According to the Child Mind Institute, “Children who are heading back to the classroom this fall are facing unusual challenges, and one of them is anxiety about being separated from their families after months of togetherness. For some kids it will trigger separation anxiety, in addition to the anxiety they may feel about leaving their safe harbor from the pandemic.”
“Kids are just really used to being home with their parents now,” notes Jennifer Louie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the Child Mind Institute. Even kids who had comfortably adjusted to being in school before the pandemic are finding it stressful to be separated now. And, she adds, “there is the added fear that other people are not as safe as we thought they were.”
For some children, the excitement of going back to school after so many months stuck at home will outweigh potential anxiety, Dr. Louie notes. “But I think the kids who already have anxiety are more prone to being more anxious going back.”
So, parents have a complicated mission dealing with all this anxiety and uncertainty: reassuring children that it’s safe to be away from them, while also encouraging them to be careful and preparing them to be flexible in case the situation changes. How do you do that? Here are some pointers from the Child Mind Institute.
- Validate their feelings: Parents should stay calm and positive. If your child lets you know that he’s worried or is having negative feelings about going back to school, reassure him that his feelings are normal. The knowledge that he is not alone in this experience will help your child feel he’s being heard and understood. Kids appreciate knowing what you’re doing to manage the situation and are willing to work together to ask and answer questions that can help them stay calm.
- Set the tone: Try to keep your own anxiety at bay so you don’t fuel your child’s apprehensiveness about returning to school in person. If your child has questions that you can’t answer, work together to find guidance from school or medical authorities.
- Help them think positively: Try to help your children focus on positive features about returning to school. What are they looking forward to? What do they hope they will enjoy each day at school with their friends and favorite teachers?
- Practice separation: For children who are anxious about being apart, experts suggest practicing separation, starting in small ways and building tolerance for more independence. Encourage your children to play independently and not rely on the constant presence of a parent.
- Have a routine: Making sure that your child has a predictable routine leading up to school can help kids, especially younger ones, feel more secure. Before the school bell rings on the first day of school, your children can practice getting up early and participating in morning routines, discussing homework expectations, and adhering to bedtime rituals.
- Emphasize safety measures: Review with your child the measures that her school has taken to put safety rules in place to minimize risk and keep everyone safe.
- Encourage flexibility: Since there is a possibility that children who start school in person may be expected to switch back to remote learning, at least for some periods of time, it’s helpful for kids to know that you’re prepared for changes that may occur.
Going back to school this year will have a new set of challenges when students return in person to campuses nationwide. Parents should review the safety rules and regulations for their children’s specific school and actively participate in keeping everyone safe.
InsureYouKnow.org
At insureyouknow.org, you can keep your family’s COVID-19 vaccination records, immunization documentation, and lists of prescriptions in a safe place.
Before You Turn the Key to Your New Home
March 15, 2021

Are you in the market for a new home?
Before buying a home, you’ll need a down payment, the closing costs, and, if you are getting a loan from a mortgage lender, proof of homeowners insurance to protect the mortgage lender’s investment to cover the costs to repair or rebuild your home if it is damaged or destroyed by a fire, lightning, a tornado, theft, vandalism, or some other covered event.
When shopping for a homeowners policy, you are encouraged to get quotations from multiple insurance companies, including your current insurer from whom you may get a better deal. You should consider coverage for your house, your possessions, additional living expenses if you’re displaced, and legal concerns if a visitor is injured at your home. In this last scenario, you may be held responsible for related medical bills, legal costs, and potential court awards up to the maximum amount determined by your homeowners insurance policy.
Keep in mind, a typical homeowners policy does not include coverage for earthquakes or floods. Depending on the location of your home, your lender may require you to add riders for additional insurance coverage for natural disasters. If you have valuable possessions, including expensive jewelry, camera equipment, or a fine art collection that exceed the dollar limits of your homeowners policy, you may need to purchase extra coverage known as a Personal Articles Floater (PAF) for those items.
Provisions of a Homeowners Policy
Your homeowners insurance policy will have the following standard elements that define the costs the insurer will cover.
· Damage to the Interior or Exterior of Your House
In the event of damage due to fire, hurricanes, lightning, vandalism, or other covered disasters, your insurer will compensate you so your house can be repaired or even completely rebuilt. As indicated above, destruction from floods or earthquakes, as well as poor home maintenance, are generally not covered and you may need separate riders if you want that type of protection. Freestanding garages, sheds or other structures on your property also may need to be covered separately using the same guidelines as for the main house.
Clothing, furniture, appliances, and most of the other contents of your home are covered if they’re destroyed in an insured disaster.
· Personal Liability for Damage or Injuries
Liability coverage protects you from lawsuits filed by others, including injuries experienced by visitors or caused by your pets. For example, if your dog attacks someone on or off your property, your insurer will cover medical expenses.
· Hotel or House Rental If Your Home Is Being Rebuilt or Repaired
If you need to vacate your home damaged by a covered event, a provision known as additional living expenses, will reimburse you for the rent, hotel room, restaurant meals, and other incidental costs you incur while waiting for your home to be repaired. Depending on the fine print of your policy, your expenses will be set by strict daily and total limits that you can expand if you’re willing to pay more in coverage.
Different Types of Homeowners Insurance Coverage
There are essentially three levels of coverage.
· Actual Cash Value
Actual cash value covers the cost of the house plus the value of your belongings after deducting depreciation (i.e., how much the items are currently worth, not how much you paid for them).
· Replacement Cost
Replacement value policies cover the actual cash value of your home and possessions without the deduction for depreciation, so you would be able to repair or rebuild your home up to the original value.
· Guaranteed (or extended) replacement cost/value
The most comprehensive, this inflation-buffer policy pays for whatever it costs to repair or rebuild your home—even if it’s more than your policy limit.
Comparison of Home Insurance Companies
When looking for an insurance carrier, consider the following tips.
· Compare Statewide Costs and Insurers
When it comes to insurance, you want to make sure you are going with a provider that is legitimate and creditworthy. Your first step should be to visit your state’s Department of Insurance website to learn the rating for each home insurance company licensed to conduct business in your state, as well as any consumer complaints lodged against the insurance company. The site also should provide a typical average cost of home insurance in different counties and cities.
· Review Each Company
Investigate home insurance companies you’re considering via their scores on the websites of the top credit agencies (such as A.M. Best, Moody’s, J.D. Power, Standard & Poor’s) and those of the National Association of Insurance Commissioners and Weiss Research. These sites track consumer complaints against the companies as well as general customer feedback, the processing of claims, and other data. In some instances, these websites also rate a home insurance company’s financial health to determine whether the company is able to pay out claims.
· Look at Claims Response Data
Following a large loss, the burden of paying out-of-pocket to repair your home and waiting for reimbursement from your insurer could place you in a difficult financial position. A number of insurers are outsourcing core functions, including the handling of claims.
Before purchasing a policy, find out whether licensed adjusters or third-party call centers will be receiving and handling your claims calls. Look for a carrier with a proven track record of fair, timely settlements and make sure to understand your insurer’s stance on holdback provisions, which is when an insurance company holds back a portion of their payment until a homeowner can prove that they have started repairs.
· Check on Current Policyholder Satisfaction
Ask any potential insurance agent for the company’s retention ratebased on the percentage of policyholders who renew each year. Many companies report retention rates between 80 percent and 90 percent. You can also find satisfaction information in annual reports, online reviews, and recommendations from friends and relatives you trust.
· Get Multiple Quotations
Request quotations from multiple insurance companies, including any insurer with whom you already do business for insurance on your automobile, boat, or other property. As a loyal customer, you may be offered a better rate.
- Ask about Discounts for Seniors
Some companies provide a special discount for seniors or for people who work from home. The rationale is both these groups tend to be on-premises more often—leaving their houses less prone to burglary.
InsureYouKnow.org
After you’ve selected your new home, submitted your down payment and closing costs, and arranged for homeowners insurance, keep a record of all these transactions at InsureYouKnow.org. You’ll also be able to keep annual records of your property tax fees, homeowners insurance premiums, any claims you file, and corresponding payments to cover damages or thefts of your property.
