Tag: FAST
Life After a Stroke: What You Should Know
May 21, 2024
A stroke affects the brain’s arteries and occurs when a blood vessel that brings blood to the brain gets blocked or ruptures. The area of the brain that is supplied with blood by the blocked or ruptured blood vessel doesn’t get the oxygen and nutrients it needs, and without oxygen, nerve cells are unable to function. Since the brain controls one’s ability to move, feel, and think, a stroke can cause injury to the brain that could affect any or all of these functions.
Everyone should know the signs of a stroke and seek immediate medical attention if you think you or someone around you is having a stroke. If you or someone you love has recently had a stroke, then it’s important to understand what happens next.
Know the Symptoms of a Stroke and act FAST
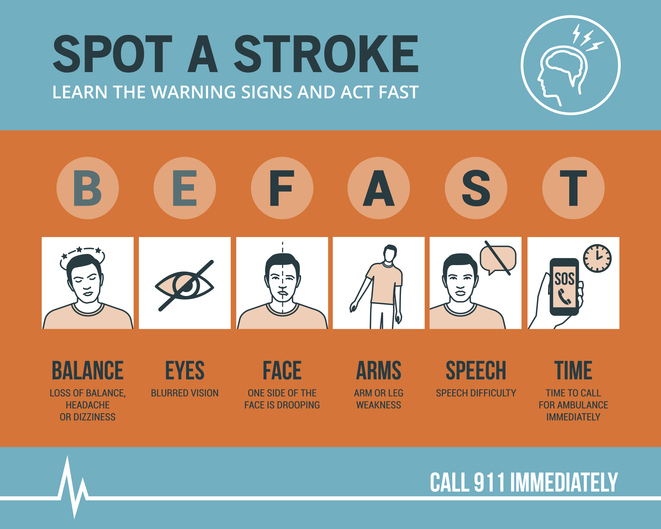
The longer the brain is left untreated during a stroke, the more likely it is that someone will have irreversible brain damage. The acronym FAST can help everyone recognize the four main signs that someone may be having a stroke and remember to act fast in seeking medical treatment. That means calling 9-1-1 immediately, as emergency response workers can treat someone on arrival if they think that person is having a stroke.
FAST stands for Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and most importantly, Time. If one side of a person’s face is drooping, if the person cannot lift both arms or one arm is drifting downward, and if the person’s speech is slurred or they cannot repeat a simple sentence, then they may be having a stroke. Not all of these signs need to be present to signal a stroke. Just one or two of these symptoms is enough to call 9-1-1, because time is of the essence in the event of a stroke.
Stroke Treatment Begins With Emergency Response Workers
Calling for an ambulance means that the emergency response workers can start life-saving treatment on the way to the hospital. Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who wait to drive themselves. The emergency workers may also know best where to take someone, such as to a specialized stroke center to ensure that they receive the quickest possible treatment. The emergency workers can also collect valuable information for the hospital medical staff before the patient even gets to the emergency room, alerting staff of your arrival and allowing time to prepare. All of what the ambulance team can provide saves time in the treatment of stroke, and in the event of a stroke, time is of the essence.
Ischemic Stroke or Hemorrhagic Stroke?
There are two different kinds of stroke, ischemic or hemorrhagic. A medical team will need to determine which kind of stroke the patient is having in order to direct treatment. An ischemic stroke accounts for 87% of all strokes and happens when a blood clot blocks a vessel supplying blood to the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel ruptures and bleeds within or around the brain.
“Fifty percent of strokes present with a clot in a large vessel in the brain, and these don’t respond very well to the old treatment, the IV clot busting medicine,” says M.D. and director of the Sparrow Comprehensive Stroke Center Anmar Razak. “And so nowadays, we do surgery, and what we do is we rush them into the hospital, into the cath lab. We quickly get access through the blood vessels and get up to where the clot is and pull it out.”
With ischemic stroke, the treatment goal is to dissolve or remove the clot. A medication called alteplase or tPA is often administered and works to dissolve the clot and enable blood flow. Alteplase saves lives and reduces the long-term effects of a stroke but must be given to the patient within three hours of the start of a stroke. Then, a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy removes the clot and must happen within six to 24 hours of stroke symptom onset.
For hemorrhagic stroke, the treatment goal is to stop the bleeding. There is a less-invasive endovascular procedure involving a catheter being threaded through a major artery in an arm or leg toward the area of the bleeding in the brain where a mechanism is inserted to prevent further rupture. In some cases, surgery is required to secure the blood vessel that has ruptured at the base of the bleeding.
Rehabilitation After a Stroke
Perhaps the most important part of stroke treatment is determining why it happened or the underlying causes of the stroke. Stroke risk factors include high blood pressure, which weakens arteries over time, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, physical inactivity, being overweight, heart disease including atrial fibrillation or aFib, excessive alcohol intake or illegal drug use, and sleep apnea. By making the right lifestyle choices and having a good medical management plan moving forward, the risk of another stroke can be greatly reduced.
That’s because if you have had a stroke, you are at high risk for having another one. One in four stroke survivors have another within five years, while the risk of stroke within 90 days of transient ischemic attack or TIA is as high as 17% with the greatest risk during the first week. This is why it becomes so important to determine the underlying causes of the initial stroke. Your doctor may give you medications to manage a condition, such as high blood pressure, and then recommend lifestyle changes, including a different diet and regular exercise.
Rehabilitation after a stroke begins in the hospital, often within only a day or 2 after the stroke. “There are so many things that patients need to fall into place to be functional and independent again after a stroke,” said Razak. “And they always come down to speed and time.” Rehabilitation can help with the transition from the hospital to home and can help prevent another stroke. Recovery time after a stroke is different for everyone and can take weeks, months, or even years. Some people may recover fully, while others may have long-term or lifelong disabilities. Stroke rehabilitation should be thought of as a balance between full recovery and learning how to live most effectively with some deficits that may not be recovered.
Difficulties from a stroke range from paralysis or weakness on one or both sides of the body, fatigue, trouble with cognitive functioning such as thinking and memory, seizures, and mental health issues like depression or anxiety from the fear of having another stroke. Everyone’s rehabilitation will look different based on their difficulties after a stroke but may include speech, physical, and occupational therapy. Speech therapy helps when someone is having problems producing or understanding speech, physical therapy uses exercises that help someone relearn movement and coordination skills, and occupational therapy focuses on improving daily activities, such as eating, dressing, and bathing. Joining a patient support group may help people adjust to life after a stroke, while support from family and friends can also help relieve the depression and anxiety following a stroke. It’s important for stroke patients to let their medical team and loved ones know how they’re feeling throughout their recovery and what they may need help with.
Stroke rehabilitation can be hard work, but just as in the initial treatment of a stroke, time matters in the possibility of a full recovery. Many survivors will tell you that rehabilitation is worth it and recommend using motivators to achieve recovery goals, such as wanting to see a child’s graduation or returning to working in the garden. With Insureyouknow.org, caretakers may keep track of medical treatments and rehabilitation plans in one easy-to-review place so that they may focus on caring for their loved one during the period of recovery from stroke.
May is American Stroke Month which aims to raise awareness of the second leading cause of death.
