Category: Health
Everything You Need to Know About Endometriosis
July 1, 2025
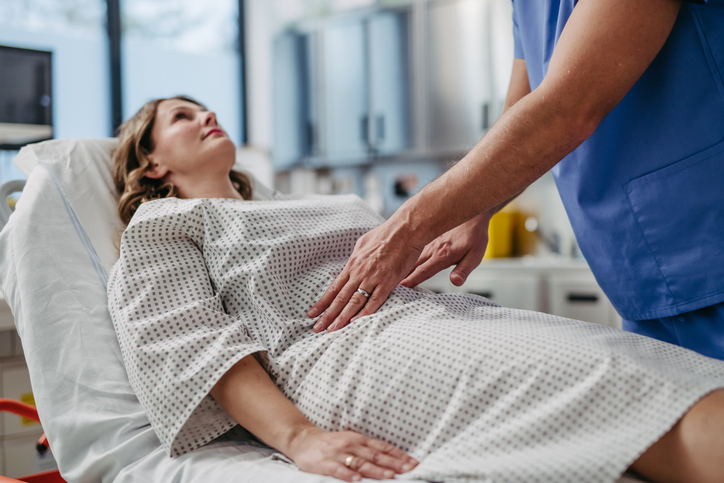
According to the World Health Organization, 10% of women worldwide, or 190 million women, are diagnosed with endometriosis. But the actual number of women who have endometriosis is likely much higher as so many cases go undiagnosed.
Endometriosis is a disease in which the tissue similar to that which lines the uterus begins to grow outside of the uterus, potentially causing pain and other complications. The main symptom of endometriosis is a painful menstrual cycle, but the pelvic and abdominal pain associated with endometriosis may eventually become chronic.
Endometriosis can begin with the first menstrual cycle and last through menopause. Because so many women are dismissed as simply having painful cycles, it’s essential to raise awareness about this condition.
If you think you or someone you know may be suffering through symptoms without a diagnosis, here’s everything you need to know about endometriosis.
What Makes Diagnosis Difficult
Women see seven physicians on average before getting diagnosed, and the average delay for diagnosis is 8.5 years. Because the symptoms of endometriosis can mimic other conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome, diagnosis is often prolonged, if even diagnosed at all. “Endometriosis is a fascinating, but troubling disease,” says Dr. Hugh Taylor, chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Yale New Haven Hospital. “It’s something that is often missed,” he says.
Another factor that makes diagnosis difficult is that the only way to diagnose someone with endometriosis definitively is through a laparoscopic procedure. Once endometrial lesions are deep enough, some may appear on an ultrasound, CT, or MRI scan. But by then, the stage of endometriosis may be somewhat advanced. Doctors may suspect the disease and clinically diagnose and treat patients for the time being. If endometriosis is suspected, the only way to a definitive diagnosis is through a laparoscopy.
What to Know About Symptoms
Besides having difficult periods each month, other symptoms include pain that becomes chronic throughout the body, digestive irregularities, bladder issues, fatigue, infertility, and mental health struggles. “We’re not talking a little bit of pain here,” says Philippa Saunders, a reproductive biologist at the University of Edinburgh. “People can’t function.”
When it comes to endometriosis, it’s important to understand that the disease is a whole-body issue. “In the past three to five years, there’s been a complete reframing of this disorder as a neuroinflammatory whole-body condition,” says Saunders. “It isn’t just about a little bit of tissue stuck in the wrong place. Your whole body has reacted.”
Because the tissue can grow anywhere outside of the uterus, endometriosis has the potential to spread throughout the body, affecting every major organ system. Many symptoms are caused by the inflammation that occurs because of the disease. This is why a patient may experience bowel issues, even when lesions are absent in the bowels.
Why You Need a Specialist
Even though endometriosis is a gynecological condition, not every gynecologist is extensively trained in diagnosing and treating endometriosis. Because the condition is so complex and largely misunderstood, even the best doctors are not equipped to treat the disorder if they don’t specialize in it.
The Endometriosis Foundation of America recommends finding a specialist that has exceptional surgical skills, access to modern techniques and equipment, a current understanding of various treatments, and an openness to complementary approaches. Since there is no known cause or cure for endometriosis yet, the best way to manage the condition is through ongoing treatment with a trusted doctor.
“For women, it can be validating to learn that all of their symptoms have an explanation and that we have effective treatments,” says Taylor. If you suspect endometriosis, you should ask your healthcare team, including your general doctor, OB-GYN, and pelvic floor therapist, if they have any recommendations for specialists in your area.
Listen to your body and remain committed to finding a doctor who will listen to you, too. Trust your intuition and ask yourself if a doctor is listening to you, acknowledging your symptoms, and addressing your concerns.
Treatment Options
If endometriosis has been confirmed through another laparoscopic procedure or it is suspected, an excision surgery becomes an option in reducing pain and preventing further complications. Excision surgery at the root of a lesion, rather than ablation, is the best way to prevent the lesions from returning.
However, the removal of lesions is not a cure. A study in the International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology found that 62% of women with endometriosis had a second surgery within two years, while half had a repeat surgery within 5.5 years.
The recurrence rate is why maintaining the condition is the main component of ongoing treatment. Make sure you have a doctor who is knowledgeable in hormone therapy, is monitoring your symptoms closely, and making lifestyle recommendations. For instance, plenty of movement and exercise, particularly pelvic floor therapy and Pilates, reduce recurrence and symptoms, while a plant-based anti-inflammatory diet does the same.
If you are diagnosed with endometriosis, then prioritizing your overall health will be the best thing you can do to manage the condition. Do everything possible to reduce your symptoms, including working with your doctors. With Insureyouknow.org, you may keep all of your research, medical records, and financial documents in one place, making the management of your endometriosis less overwhelming.
What to Do After a Loved One Dies
June 15, 2025
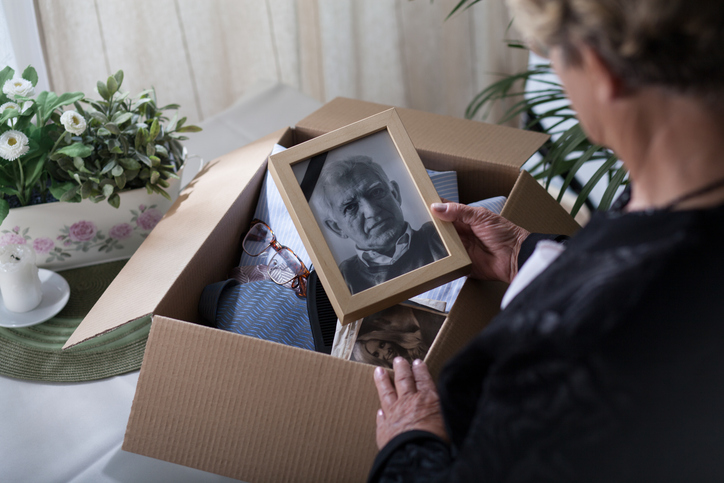

The loss of a loved one is one of life’s most stressful events. Almost ninety percent of people over the age of 16 have experienced grief, but 57% of Americans have experienced a significant loss within the last three years.
Mourning is the natural process someone will go through when a loved one passes away. Though many initially gather with friends and family to share the loss, the mourning process is personal and may last months or years.
Here are some gentle steps to take when processing the loss of a loved one.
Know the Symptoms of Grief
Dealing with death is something most people would rather avoid altogether, but grieving isn’t something to put off. Your grief is likely to be felt physically, emotionally, and psychologically. Allowing yourself to move through your feelings is integral to the process.
Give Yourself Time
Now is the time to take care of yourself. You don’t need to put an expiration date on your grieving. “Some people grieve for years, and while they become more functional as time goes on, they may still get hit out of nowhere with grief-related feelings,” says Dr. Judy Ho, host of the podcast Supercharged Life.
“Grief isn’t linear; it’s more circular. You may feel like you’ve accepted the loss, then something happens months later, and you circle back to denial,” says Ho. However long it takes you to begin feeling better is unique to your situation. So be gentle with yourself as you experience waves of mourning.
Routine is Everything
It is essential to develop and stick to a new routine. Many activities will feel different, and it’s okay to make changes accordingly and try new things. However, sticking to some of what’s normal for you can also be a great comfort. “Grief has a way of rocking our sense of safety, but routine creates stability, which often codes as safety,” says Dr. Anita Robinson, author of The Gift of Grief.
Lean on Your Support System
When a loved one dies, it affects everyone in their circle. “Don’t manage grief alone,” says Melissa Robinson-Brown, a clinical psychologist in New York. “If there were ever a time to lean on family and friends, this would be it.” Talk to those you feel most comfortable with and let them know what you’re experiencing.
While everyone finds their way to cope, it can be valuable to share the loss of someone and grieve together. People should be open and honest with one another and not try to hide their feelings. Because the roles of family members may change, it’s best to communicate with one another moving forward.
Bereavement Groups and Counseling
It may be helpful to join a bereavement support group. Bereavement means the state of having been deprived of something or someone valued, primarily through death. Being around others experiencing the same loss level helps many feel less alone. Hospices, hospitals, and community organizations will all have more information on support groups in your area.
One-on-one counseling can be an essential part of losing a loved one and processing that loss in a healthy way. Death can come as a great shock, and mental health counselors can offer a safe place for you to resolve those emotions. Through hospice, bereavement care is even provided for up to 13 months.
Experiencing the loss of a loved one can be a painful process. Focusing on the joy the relationship brought to your life is a great source of solace during the most emotional moments. With Insureyouknow.org, you may store your loved one’s records for safekeeping so that when it’s time to handle the logistics of someone passing, you’ll be up for the task.
Everything to Know if You Want to Live and Age in Place
June 1, 2025
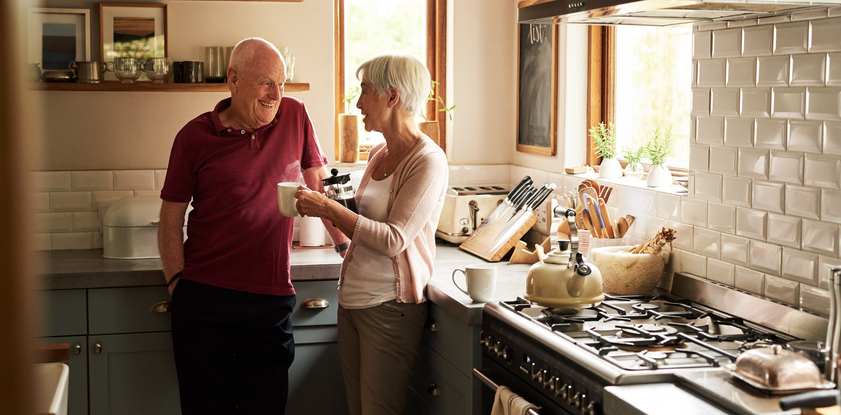

Most people would prefer the comfort of having their own space as they age. Studies show that as many as 90 percent of adults wish to remain home. Living in place, sometimes known as aging in place, also equates to maintaining independence for as long as possible.
“For many of us, home is comfort. There’s a history we are familiar with: It’s family, friends and neighbors. It reflects our culture and our community,” says Emily Johnson, a licensed clinical social worker. “As we begin to lose control of other aspects of our life, staying in our home says, ‘I can accept help, but I am still running the show.”’
Remaining home as you grow older requires careful consideration and thoughtful planning. Here’s everything you need to know about living and aging in place.
Make Your Plans Now
The best thing to do if you want to age in place is to plan for it now while you are still able to. Consider what kind of help you may need now or want in the future. Planning ahead gives you time to set up your home and budget for the required changes and services.
Be sure to factor in any health conditions you or your spouse may already have. Think about how that condition may make it difficult to care for yourself independently. Then, talk to family and friends about what level of support they can offer. Ensure everyone’s realistic and plan to revisit the issue periodically over time.
On average, an adult over the age of 65 falls every second in the U.S. You can prevent accidents at home with these simple safety measures:
- Apply contrasting colored electrical tape on stair landings.
- Remove throw rugs without grip from the home.
- Clear away clutter, including loose cords.
- This includes the outdoors; porches and walkways should be swept and shoveled.
- Ensure the home is well-lit and place night lights in halls and bathrooms.
- Always use handrails and install grab bars in showers and tubs and next to the toilet.
- Always wear proper-fitting supportive shoes in the house and outdoors.
As conditions change, you may need to reassess your home regularly for potential hazards. To troubleshoot, ask a family member or friend to complete a walkthrough with you for a second set of eyes.
Budget For Services
Home-based care services can be used in short-term situations, such as during recovery from surgery, or in the long term for those who need ongoing help. In addition to healthcare services, people may need help with chores, meal delivery, or transportation for doctor’s visits.
While home-based services can be expensive, they may cost far less than moving into an assisted living facility. The Eldercare Locator is a resource that connects people to caregivers through local support services.
People often rely on various payment sources, including personal funds, long-term care insurance, and government programs. For more information on government-based healthcare and financial assistance, visit USA.gov.
Prioritize Your Long-Term Health
If your goal is to stay home, then make your overall health maintenance a top priority. Stay current with your doctor’s visits and set alarm reminders for medications.
Make a plan to maintain body strength as you age, powerful legs to support balance and assist you in getting up safely from a seated position. “Strength, balance, and flexibility exercises are key to preventing falls, which are among the greatest threats to our healthy longevity,” says Scott Kaiser, a family physician and geriatrician.
In addition to scheduling regular exercise into your routine, don’t forget about your mental well-being. “Investing in meaningful relationships is one of the most important things we can do to increase our health, quality of life, and wellbeing,” says Kaiser. Remain engaged in social activities and plan visits with loved ones, including video calls with those who live farther away.
Prepare for the Unexpected
Always be prepared for unexpected events and medical emergencies. “Be proactive,” says Johnson. “Where are there gaps now or barriers to living independently in the future?” For instance, if you have a preexisting allergy or medical condition like diabetes, wearing a medical alert ID bracelet is a simple precaution. A wearable electronic monitor that can alert emergency personnel in the event of a fall is another easy measure to implement.
Even if the plan is to stay at home for as long as possible, there may come a time when that’s no longer safe. The decision about whether or not to move away from home is a difficult and emotional one to make.
It’s best to mentally prepare for that possibility now while there’s still time to have some control over where you’ll go. Learn as much as possible about the available housing options and include loved ones in the search.
Living in place is an attainable goal with the right amount of forethought. At Insureyouknow.org, you may store all of your financial and medical records in one easy-to-review place. By staying on top of your budget and health needs, you will have already taken care of the most critical components of your aging-in-place plan.
Choosing the Right Care Center for Loved Ones
May 15, 2025
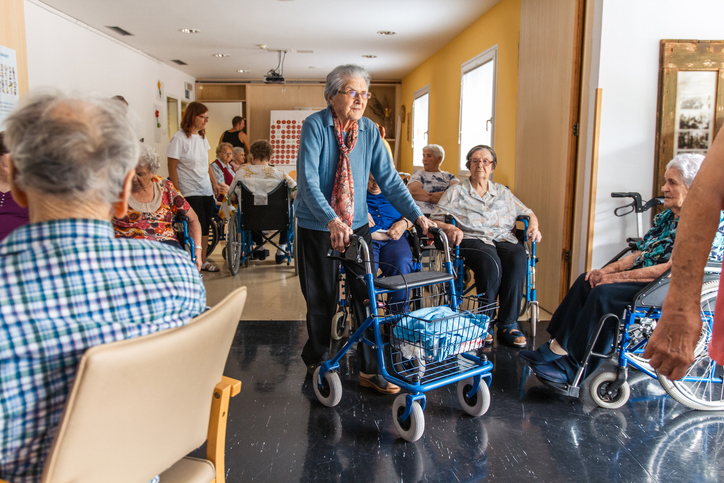

Moving a loved one into a care facility is an important decision that requires careful consideration. Choosing the right one takes in-depth research to determine if it’s a good fit for the individual’s needs. There are nearly 31,000 assisted living centers in the U.S. The first step in finding care is understanding the difference between types of facilities and whether they can provide the level of attention the patient needs.
Types of Care Centers
A nursing home provides around-the-clock medical care for individuals who will likely remain there until their passing. These are meant for individuals who can no longer care for themselves independently or be cared for by their loved ones at home. A skilled nursing facility may be intended for a short or long period. Still, it provides a higher level of medical attention and is usually for those recovering from surgery or an illness.
Independent living and assisted living centers are for those who need less intensive medical assistance but still require some level of care. A continuing-care center can serve as an intermediary between assisted living and a nursing home. For individuals who need 24/7 care and supervision due to Alzheimer’s or dementia, there are memory care centers that specialize in those specific needs.
Paying for Long-Term Care
Many people are unaware that there is no federal assistance available for long-term care costs. There is one exception in which Medicare will pay for the first 100 days in a nursing home or skilled nursing facility if the patient has been hospitalized for at least three consecutive days within the last year before needing to be transferred to a care facility.
Paying for care can be a significant issue for families as it can become costly. “Nursing homes are one of the most expensive levels of care,” says Amie Clark, a senior care expert. “And most people don’t have that kind of money.”
Long-term care insurance policies may be a wise, proactive investment, but they can also be expensive. In most cases, people pay privately or out of pocket until their resources are used up. According to the NCHS, 62% of nursing home residents use Medicaid as their payment source.
Other Factors to Consider
Unfortunately, nursing homes face their fair share of challenges, such as being understaffed or dealing with infectious outbreaks. This is why it’s so important for families to do their due diligence in researching facilities and not feel rushed into making a decision.
Medicare offers an online resource to find and compare nursing homes, hospitals, and other care facilities in your area. It uses a five-star rating system and provides information about each nursing home, including vaccination rates and inspection reports. Another helpful resource is the Nursing Home Inspect, which compiles nursing home inspection reports.
Experts suggest not relying on ratings alone and focusing on a facility’s staffing, saying that nothing beats an in-person visit.
Here’s what to do when you’re on-site:
- Speak with a range of employees, from administrators to activity managers to culinary directors.
- Take note of response times.“How long does it take for call lights to be responded to?” says Shannon Gimbel, manager of the ombudsman program for Denver’s Area Agency on Aging. “Are residents standing in hallways waiting for medication?”
- Notice the patients’ level of hygiene. “Listen in the hallways,” says Tony Chicotel, attorney for the patient advocacy group California Advocates for Nursing Home Reform. “Look at the hair, clothing, teeth, and fingernails of the residents.”
- Try the food. Sit in the dining hall with other residents and observe the interactions between patients and staff.
- Ask about the activities offered to residents and consider whether or not they will be intellectually stimulating.
While it’s best to find a care facility that’s close to you, traveling farther for the best fit may become necessary.
Once you determine what kind of facility your loved one needs and make payment plans, then you should do your research and take the time to visit all of the centers you’ve narrowed down on your list. With Insureyouknow.org, you may compile your research, keep track of finances, and store your loved one’s medical records in one easy-to-review place. While it will take some research, finding the right place will provide you with invaluable peace of mind.
How Much Sleep Do You Really Need?
May 1, 2025
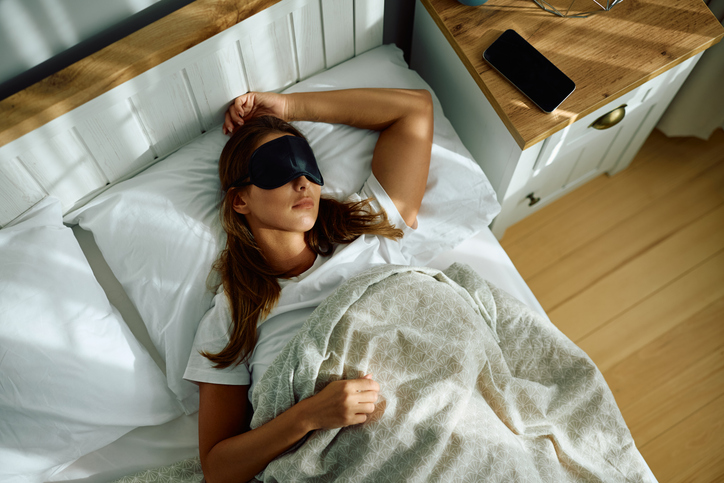

You might pride yourself on burning the midnight oil or think you’re functioning fine on five or six hours of sleep—but your body would likely disagree. According to the CDC, a third of all adults in the United States report that they don’t get enough sleep, and that’s troublesome since the benefits of a good night’s rest are numerous. Sleep isn’t just downtime—it’s when your brain files memories, your body repairs itself, and your mood resets.
So how much sleep do you actually need to feel your best? It’s not a one-size-fits-all answer. While many people are under the assumption they can operate on less than seven hours of sleep a night, research shows that seven hours is just the bare minimum needed.
Here’s everything you need to know about how long you should aim to sleep nightly.
Seven Hours Isn’t Exactly the Golden Rule
According to the CDC, the average adult between the ages of 18 and 60 needs at least seven hours of sleep. “Some people need less than seven hours, while others might need more,” says Eric Zhou, a psychologist at the Division of Sleep Medicine at Harvard Medical School.
While people usually focus on the amount of sleep they need, they forget to consider the quality of sleep they’re having. For instance, you may go to bed at 11 p.m. with an alarm set for 6 a.m., but when do you actually fall asleep, and are you staying asleep all night?
“Instead of focusing exclusively on the number of hours we sleep per night, we should also consider our sleep quality,” says Zhou. It’s about the time you spend in bed every night, but it’s more about the amount of uninterrupted deep sleep you’re experiencing nightly.
Wearable sleep trackers, such as the Oura Ring, Fitbit, or Apple Watch, can provide valuable insight into your patterns and help you develop better sleep habits.
Women May Require More Sleep
The traditional estimate of nightly seven to nine hours of sleep is based on studies that only involved men. This has recently led many to wonder whether or not women need more sleep than men, and several factors suggest they may.
Since women are often caregivers, they are wired to multitask and use more of their brain, while they also report higher levels of stress. This mental exhaustion alone could account for them requiring slightly more sleep every night.
The other factor is hormonal, depending on where they are in their cycle each month, as well as during pregnancy and even after menopause. For instance, the hormone progesterone, which peaks at different times, is a relaxing hormone and often leads to drowsiness.
While not everyone agrees, many health professionals are beginning to recommend more sleep for women, who probably need at least eight hours of sleep a night.
Factoring in Age
The younger you are, the more sleep you need, especially when the body is growing or going through major changes. A newborn needs up to 17 hours of sleep a day, while a teenager between the ages of 13 and 18 needs up to ten.
As you age, melatonin production, which is the sleep hormone, declines. The result of less melatonin is waking up earlier or waking up throughout the night. Once over the age of 61, getting the recommended amount of nine hours of sleep can become more challenging.
How to Get a Good Night’s Sleep
Consistency is key for a good night’s sleep. Try maintaining the same time window between lying in bed and waking up. This works because the body recognizes routine and can be trained to sleep within a specific time frame. “People with good sleep quality often have a predictable sleep window where their sleep occurs,” says Zhou. “Good sleepers are likely to sleep around the same number of hours and stay asleep through the night.”
Physical activity during the day also influences how well you sleep at night. The more activity you incorporate into your day will directly correlate to how much sleep your body needs and therefore, how tired you’ll be by bedtime. “Activity increases your sleep drive,” says Dr. Michelle Drerup, a sleep medicine psychologist. “It’s important to develop exercise as a habit. Pick a time of day that works for you and exercise at the same time every day.”
Refraining from eating two to four hours before bedtime can also help. When we eat, the body must switch gears to digestion, so when you eat right before bed, you must focus on digesting that food and cannot fall into a deep sleep. Eating before bedtime robs your body of its capacity to concentrate on the work it does while you’re sleeping.
The same rule applies to nightly screen time. Studies show that two or more hours of screen time in the evening can disrupt the rise in melatonin you need to fall asleep. Turn devices off at least one hour before bedtime, and replace scrolling with reading a book, taking a bath, or meditating. If you must use your phone at night, reduce your blue light exposure by turning down the brightness or switching to nighttime mode in the evening.
Building a routine that you can stick to ensures the right amount of sleep every night is possible. With Insureyouknow.org, you can store your medical records in one easy-to-review place. The effort you put into a good night’s rest will show in time.
Everything to Know About Equine-assisted Psychotherapy
March 14, 2025
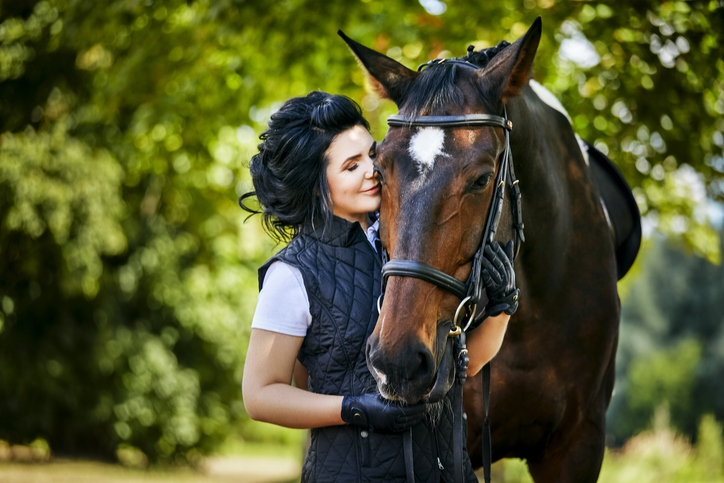

Horses are well known for the special connection they form with their owners, but bonding with horses is not only more accessible than ever, it can be healing. Beyond pet companionship, horses can be used in therapeutic settings to help people process challenging emotional experiences.
During equine-assisted psychotherapy (EAP), people may groom, feed, or lead a horse with a mental health professional nearby. The main goal of this form of therapy is to help patients with emotional regulation. EAP differs from traditional talk therapy as it offers a more inviting setting, brings people outside, and allows them to use all their senses while processing emotions.
How Horse Therapy Differs From Traditional Counseling
Unlike humans, horses bring different qualities to therapy. For example, horses cannot give patients a feeling of bias or judgement, but because they are sensitive to emotions, they still convey a sense of understanding and connection. “They’re sentient beings, and they think and feel and have incredible memories,” says Paige Deponte, director of an equine-assisted trauma-informed care organization in Honokowai, Hawaii. “They were made to do this.”
Plus, horses’ care, such as feeding and grooming, is therapeutic and helps build empathy. The horse’s unique nature gives people a better awareness of their emotions, increased adaptability, stress tolerance, and even self-esteem. “The goal is for the client to find out more about their needs through a series of questions,” says Depontei. “No session is ever the same.”
Horses Have Been Used in Therapy Throughout History
Hippocrates, the Greek physician known as the “Father of Medicine,” wrote about the therapeutic benefits of horseback riding around 400 BCE. Around the world, horses have even been used to heal specific physical ailments. Scandinavia used equine therapy to treat patients with myelitis in 1946, and in 1952, the Olympian Liz Hartzel credited the healing power of horses as helping her recover from polio.
Riding became a popular form of therapy in the 1950s and 1960s. The North American Riding for Handicapped Association was formed in 1969 and eventually became the Professional Association of Therapeutic Horsemanship International, recognized as PATH. By the 1980s, American and Canadian therapists created a more structured Hippotherapy model to be referenced for treatment.
The Benefits of Horse-Assisted Therapies
Equine-assisted forms of therapy are becoming more popular because of increasing evidence of their effectiveness. “I think it’s growing, and the benefits of it are commanding attention because it is unique,” says Whitney Diamond, who breeds and trains horses for a living. “A huge part of the reason why I believe that the therapy is so powerful with horses is that they’re so primal.”
It’s thought that since they’ve been domesticated for some time, horses are attuned to human emotions and nonverbal signals. This allows them to mirror what someone is feeling, enabling the patient to recognize their mental state. “A big part of therapy is that you must work with them,” says Diamond. “It’s powerful because you have this other being that’s not judging you, that’s working off synergy and energy, and they’re going to meet you where you’re at, good or bad.”
EAP is shown to be just as effective in children, teens, and adults and may be used to help with anxiety, depression, and trauma. EAP can benefit young children who find it challenging to open up and process painful experiences.
There are also physical benefits from working with horses. Caring for an animal is shown to decrease blood pressure and improve cholesterol levels. Horses in particular encourage socialization through other riders, which can lessen feelings of loneliness and isolation. Vigorous horseback riding is also a great cardiovascular exercise, while grooming the horse and taking care of equipment can help build strength.
How to Find a Treatment Center Near You
You may reference PATH Intl. or the Equine Assisted Growth and Learning Association to find an EAP certified professional. These are the most reputable organizations that set the standard, train, and certify anyone using horses as a part of therapy.
Those who are interested in trying EAP are advised to find a program that specializes in their specific difficulty, such as anxiety or trauma recovery. The mental professional at the given organization will then be able to tell potential clients whether or not they seem like a fit for the program.
If you have any physical limitations, especially back injuries, then EAP might not be the right fit for you. Other considerations include a fear of horses and the cost of therapy, which may not be covered through insurance.
If you or a loved one may benefit from equine-assisted therapy, you may look for an organization that takes your insurance or offers affordable care. With Insureyouknow.org, you may keep your medical records and progress reports in one easy-to-access place. By keeping track of the changes you notice during therapy, you can observe how you benefit from this unique form of connection in many different ways.
Lost a Job? Find Your Career Instead
March 1, 2025

After the shock of losing a job subsides, how can you ensure you are career-ready to jump back into the job market?
It’s important to remember that a job isn’t a career. A job is a piece of work you take to pay living expenses. A career is a long-term professional project that can span multiple jobs and pivots throughout your lifetime. For example, someone who loves working with numbers may take a job as a bookkeeper, but they want to build a career as an accountant. Even if they lose the bookkeeping job, they can still pursue the career of being an accountant with further professional development.
With 4 out of 5 workers worried about losing their job in 2025, changing your thoughts from “job search” to “career path” is the path forward. Here are some tips to ensure you are career-ready.
Take Time for Reflection
“Take the time to reflect on where you’ve been and where you want to go before jumping back into the job search,” says Sabina Sulat, author, podcast host, employment expert, and influencer. “If you don’t know where you’re headed, you can’t reach your goal.”
By taking a moment to consider the best next step in your career, you can avoid the trap of signing up for the same qualities that made you sigh with relief when you lost your last job.
Learn a New Skill
As you build a career, adding new tools to your skillset make you a more valuable employee. According to a study published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, people who pursue mastery of a skill experience a more positive attitude and better sleep than those who just exercised or did nothing to alleviate the ongoing anxiety of job loss. Look around and see what skills to acquire to secure your next step in your career.
Pivot
A November 2024 Gallup poll reported that 51% of employees are dissatisfied and actively seeking a new job. Perhaps this last job revealed something you didn’t enjoy about your chosen career path. Now is the time to pivot! This time between jobs can be used to learn about another aspect of your career you hadn’t considered and pursue other opportunities.
Figure Out What You Want…And Ask for It
According to Eric Maisel, psychotherapist and author of Choose Your Life Purposes, we’re naturally reluctant to ask for what we want. “That reluctance at best reduces your enthusiasm and makes for a dry presentation, and at worst it prevents you from reaching out to your connections or to the jobs that interest you,” he says. “On top of all of the practical realities involved, the psychological ones matter a lot, too!”
Do the necessary research to determine what you want, monetarily and career-wise, and practice asking for what you need. You can do this by setting up practice interviews with friends and colleagues, journaling your thoughts, and practicing saying the words in front of a mirror.
Doing the necessary work to make yourself career-ready helps you realize your goals. “This clarity and confidence not only make you a stronger candidate but also shine through in your applications, interviews, and networking conversations,” says Sulat.
InsureYouKnow.org
With the recent rise in layoffs and higher unemployment, you must remain ready to pivot. After you’ve gathered your certifications and updated your resume and portfolio, store them safely using InsureYouKnow.org to keep them organized and easily accessible. Having these important documents at your fingertips makes accessing that next step on your career journey easier.
Medicare Grocery Allowances: Who Qualifies and Is it Worth it?
January 15, 2025

In 2020, the Medicare Advantage expanded coverage benefits for those with chronic conditions, such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, end-stage renal or liver disease, heart disease, and more. The coverage expansion is referred to as the special supplemental benefits for the chronically ill or SSBCI. Some additional benefits include food allowances and prepared meals, but in some instances, they may even include over-the-counter medications, transportation, and in-home support services.
If you’re interested in receiving a grocery allowance or meal benefits or need food assistance, here’s everything you need to know about the additional coverage.
How the Medicare Grocery Allowance and Meal Benefits Work
Grocery allowances and meal benefits are not the same. If you qualify for grocery allowances, they are issued through prepaid debit cards on a monthly or quarterly basis. While the grocery allowance varies by state, it is usually $50 each quarter.
Under the CHRONIC Care Act, as of 2020, Medicare Advantage plans could also provide meals anytime to keep eligible recipients from needing hospitalization. Meal benefits are often more popular than grocery allowances, but it’s usually only offered for a limited amount of time, which is typically four weeks after a hospital stay.
Knowing Which Plans Offer Food Assistance
Not all Medicare Advantage plans include food allowances, so it’s important to determine if you qualify before choosing a plan. Traditional Medicare Part A and Part B and Medicare supplement plans, which are meant to supplement gaps in coverage, do not offer a grocery allowance. Some Part C Medicare Advantage Plans do offer grocery allowances and meal benefits, such as special needs plans or SNPs and dual-eligible special-needs plans D-SNPs. D-SNPs are meant for Medicare members who are also enrolled in Medicaid and who have a chronic condition. Those with Medicare Advantage plans who are disabled or who have a low-income subsidy or LIS may also be eligible to receive grocery benefits.
The CHRONIC Care Act of 2020 gave Medicare Advantage plans the ability to offer non-medical benefits such as funds for groceries. “Therefore, the Medicare Advantage plan can decide if they want to provide those benefits, and those benefits have to be designed only for the chronically ill,” says Alexandra Ashbrook, director of the Food Research and Action Center. “The non-medical services have to be targeted to people who have at least one chronic health condition, such as those at risk of hospitalization or some other adverse health outcome requiring intensive care coordination,” she says.
Qualifications for the grocery and meal benefits vary by plan, so it’s important to check with the plan’s provider to see what they offer and if your health condition qualifies. Choosing a plan based solely on food allowances isn’t the best approach over the long run. So, even if the plan offers a grocery or meal benefit, it may not justify what you pay for the plan. Whether or not the plan covers medical needs should always be the priority. Take into account every benefit the plan offers before making a decision.
What to do if You Don’t Qualify for Medicare Food Allowances
There are still other options for those who do not qualify for the grocery allowance through their Medicare Advantage Plan. Low-income seniors 60 or older can apply for food assistance through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program or SNAP. Many people don’t even realize that they qualify for these benefits. “Unfortunately, only about 48% of eligible older adults are participating in SNAP,” Ashbrook says. “That’s a really important gap that health care providers and health systems could help to close before looking at any of the other additional food programs.”
Those who are 60 or older and have an income below 185% of the federal poverty income guidelines may also qualify for the Senior Farmers’ Market Nutrition Program SFMNP or the Commodity Supplemental Food Program or CSFP. The SFMNP provides coupons for fresh fruits and vegetables, which can be used at farmers’ markets and community farms, while the CSFP is a monthly package of healthy food that the USDA distributes to local agencies for participants to pick up. If eligible, some states even offer package deliveries.
To find out if you are eligible for SNAP or either of these additional programs, you may fill out an application online. If you’re a veteran, for instance, you may be more likely to qualify for USDA food assistance programs. Even if you are not eligible for Medicare grocery allowances, SNAP, or other supplemental programs, you still have options. Meals On Wheels is another program designed to help low-income seniors access prepared meals. The meals are provided on a sliding scale based on a recipient’s income to make them an affordable option for those in need.
If any food assistance will help you, then exploring every available benefit will pay off. Whether it’s a Medicare food allowance or a USDA-based food assistance program, helping purchase and prepare healthy foods can go a long way in improving the quality of your everyday life. With Insureyouknow.org, you may keep track of your applications, health records, and grocery budgets in one easy-to-access place for all your meal planning needs.
The Health Benefits of Even the Shortest Vacations
December 15, 2024

Just like an athlete benefits from breaks during exercise, vacations are an important part of someone’s well-being. According to a Pew Research Center survey in 2023, nearly half of the U.S. workers surveyed said they take less time off than the paid time off their employers gave them, while globally, eighty-five percent of workers reported that vacations make them feel more optimistic and that regular vacations are important for their overall health.
“Not taking time off from work to go on vacation or simply rest can lead to overwork and burnout,” says Joyce Marter, a licensed psychotherapist. “People should use all the vacation time allotted to them—and sick days should also be used.
If you’ve been feeling the need for a true rest, here’s everything you need to know about getting the most out of even the shortest vacations.
The Right Amount of Time Off
While experts agree that any amount of vacation time is beneficial, three weeks per year may be just the right amount to benefit your health. The European Society of Cardiology conducted a 40-year-long study that found people who take less than three weeks of vacation time per year have a 37% greater risk of premature death, even despite living an otherwise healthy lifestyle.
Another study in 2020 showed that people who split two weeks of annual vacation time into five short breaks had a 24% lower risk of metabolic syndrome. Even the long weekend can come with serious benefits, as those who took a four-day vacation had improved stress-levels for an entire month after returning to work.
Since the positive effects of a trip usually fade after a month of being back home, taking several short trips throughout the year can be more beneficial than one or two long vacations. Plus, the planning process can make you feel happier than the trip itself, so allowing yourself to plan and look forward to a trip more often throughout the year extends the benefits of your vacation time even more.
The Right Way to Travel
Simply going on vacation won’t necessarily result in feeling as though you have a break. “I’ve heard countless times how exhausted people are when they come back from their vacation and feel like they ‘need a vacation from their vacation,’ and that’s because many times we pack so much into a very short amount of time,” says Esther Susag, a travel blogger. “We want to see everything, do everything, and not waste a minute.”
In order to benefit from any amount of time away, it’s important that you provide yourself with the opportunity to actually rest.
Slow travel is a more meditative approach to traveling that allows people to slow down, as the name suggests, and literally stop and smell the roses. “If you want to really unplug and relax without the stresses of traveling then slow travel may be for you,” says Mark Wolters, a YoutTube travel channel host. “You get to unpack your suitcases less, take fewer planes, trains and automobiles and just relax in a destination.
Once you’re on vacation, give yourself the gift of a loose plan. Do some research ahead of time and bring a list of some things you don’t want to miss when you’re there, as well as a few restaurant possibilities. For every day that you’re there, have a half day’s worth of activities planned, giving yourself the time and space in each place to really enjoy the experience.
The Right Companion
In order to have a truly beneficial break, it becomes important to choose the people you vacation with carefully. “Spending time with family and friends are all things that we know can increase well-being and even reduce stress,” says Stephanie Preston, psychology professor at the University of Michigan. “There can be a lot of interpersonal conflict over how you manage the schedule and the priorities.”
While the idea of traveling with extended family, for instance, seems like a good idea on paper, trying to please everyone may prove to be the opposite of a relaxing getaway.
That being said, vacations can also provide the opportunity to bond with your family members and create truly lasting connections with one another. When you plan to travel slowly, your adventure becomes more about being together as a family than about visiting as many attractions as possible. Slow travel provides the space not only to notice your surroundings but also to notice the people you are seeing them with.
The Right Location
Once you decide who to travel with, opt to stay at a vacation rental rather than a hotel. Rentals are rarely at the center of the tourist attractions. This provides both a more relaxing environment to unplug in but also immerses you more deeply into the local experience. Plus, with rentals that have fully stocked kitchens, there’s less of a reason to have to leave and more of an opportunity to stay in and unwind.
The Right Format
Most people intuitively sense that taking a break is good for their health. What’s most important for people to realize is that they don’t need a vacation to have a break. “Many people don’t often have a choice in how much rest is available to them,” says Julia Kocian, a social worker and mental health counselor. “The way society is set up, we treat rest as a privilege, not a right,” she says.
Whether it’s taking a walk in the evening or meditating while you fold the laundry, only you will know what activities best help you to relax. “I view rest as intentionally slowing down or stepping away from an activity, while taking a break can be more active, like going on a walk or stretching,” says Samantha Artherholt, a psychologist and professor at UW School of Medicine. “The goal of any sort of rest or break is it should feel relaxing. You should feel refreshed and better after the break than you did before.”
Work yourself up towards taking more vacation time by finding ways to distribute downtime throughout your day and week. “The biggest thing is giving yourself permission to do it,” Artherholt says. When you learn more about what feels like rest to you, then you can start planning a handful of short vacations for yourself throughout the year. With Insureyouknow.org, you may store your destination research, savings goals, and travel plans all in one place. Remember that planning for your next vacation may be over half of the fun.
Volunteering for Seniors: Benefits & Opportunities
November 15, 2024
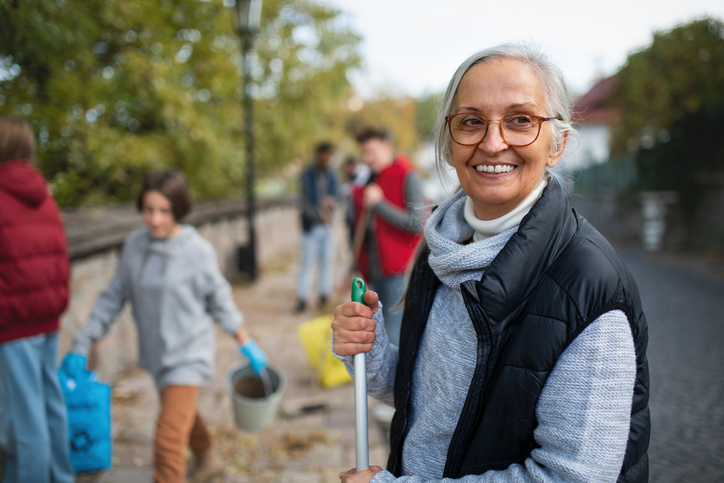
There are good reasons why more than one in five older adults volunteer. A study in the Australian Journal of Psychology found that the more people volunteer, the more their overall life satisfaction increases.
If you find yourself with the urge to help or give back to your community somehow, here’s everything you need to know about volunteering later in life.
Volunteering can improve your physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. The American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that if someone volunteered for at least 100 hours per year, or less than two hours a week, for at least four years, they experienced a reduced risk of mortality, less physical functioning limitations, higher amounts of physical activity, and positive psychosocial outcomes, such as a stronger sense of life purpose. “Volunteering is an affirmation that your time hasn’t ended. It’s also a way to affirm that careers are ongoing,” says Marcia Wall, a career coach. “Continue your career through volunteering, and you’ll continue to have that sense of professional identity that can continue even without getting a paid job,” she says.
Furthermore, volunteerism can prevent social isolation and loneliness, major risk factors for mortality among the aging population. In addition to having the opportunity to utilize the skills you already have, volunteering can provide the acquisition of new skills and knowledge, too. “It’s good for the mind, and for socialization; it’s the idea that we’re all lifelong learners,” says Wall. “There is value in learning for learning’s sake. The idea that our brains and our spirits are still active and you can’t be curious without having a spirit. It’s an affirmation that your time hasn’t ended,” she says.
What to Consider Before Getting Started
Before choosing a volunteer opportunity, think about your “why” and what kind of work you want to do. Read about an organization’s mission and the ways they go about achieving that. Does the work they carry out align with your values? Volunteering is a way to engage with your interests, so make sure that you look for an organization that makes you feel excited and even motivates you.
Then, check the reviews. Pay attention to positive and negative feedback and how the organization responds. Beware of any place that uses phrases like “work tirelessly” or seems understaffed or over-extended. “First and foremost, volunteers should not be considered ‘free labor,’” says Wall. “Volunteers are skilled and valuable contributors who are choosing to donate their time in exchange for a personal reward of some kind,” she says. Ultimately, it’s important for you to feel in control of the work you decide to do. Remember that it doesn’t have to be long-term; you can always pursue other avenues. Volunteering should never feel like a chore.
Six Options for Older Adults Looking to Volunteer
There are volunteer opportunities out there for everyone. Here are several ideas to get you started on your search.
- Local or National Charities
Always look at what’s in your backyard first. Habitat for Humanity, for instance, exists nationwide and helps families in your community establish stability and self-reliance by providing them with homes. Food banks always need assistance with daily tasks such as food delivery and donation gathering. Feeding America lists food banks in your area where you can begin. Charity thrift stores are another great way to help with a cause you care about. The items sold there benefit those who buy them, and the proceeds go toward the organization’s efforts.
2. Local, State and National Parks
The National Park Service is often eager to have new volunteers. Opportunities include helping with one-time special events or long-term commitments that involve tasks such as invasive plant removal or serving as a tour guide and educator.
If pets are your passion, working with your local animal shelter may be the right fit for you. While large, well-known organizations like the SPCA and The Humane Society of the United States are great places to work with, smaller local rescues need help, too. Volunteering with a rescue center may involve caring for and playing with animals, providing potential the public with information, cleaning, and helping at fundraising events.
4. Fostering Younger Generations in a Multitude of Ways
Did you know you could become a foster grandparent for a child living in your community? Fostering a child usually consists of tutoring, mentoring, and caregiving. If that kind of opportunity sounds rewarding, check with your local churches and Americorps for children in need of a foster.
Your local schools are another venue to check with for volunteering to help teachers, tutor children, or chaperone field trips. Eldera is another program that connects those over age 60 to help students with homework, while Big & Mini connects people with common interests intergenerationally. Yet another group is Career Village, which brings former professionals to students interested in those careers. If sports are of interest to you, then coaching a youth team is yet another way to give back to children in your backyard.
5. Providing Companionship to Older Adults
There are several ways to help people your own age, such as volunteering with your local Hospice agency. Hospice opportunities include being a companion to patients at the end of their lives, helping with clerical duties, or making things like fidget mats and quilts for patients. “You’re one on one with a patient or them and their family,” says Erin Long, a hospice volunteer services manager. “It’s individual volunteering and independent volunteering. We look for someone who is comfortable in independent situations.”
There are other ways to assist older adults, including being a companion to someone still living independently at home but needing a little support. Seniors Helping Seniors is just one organization that connects seniors to volunteers in their area. Hosting a meet-up for seniors in your area is another way to connect with people your age, build community among older adults, and even prevent loneliness. Starts at 60 Meet Ups helps volunteers host casual gatherings at coffee shops.
- Community Gardens
If you have a green thumb, gardening might be the right cause. Community gardens can contribute healthy foods to their community, beautify your hometown, and provide you with some health benefits. Working in the garden improves both physical and mental well-being. If your neighborhood needs a garden, then AARP can help you get one going.
Senior Corps links seniors with thousands of opportunities. And don’t forget about checking with family and friends, who may know where the local needs are. With Insureyouknow.org, you can keep all of your volunteering research in one place, as well as schedules and logs of the benefits you notice and your impact. Just remember that every act of kindness can create a lasting impact, no matter how small or large. If you’re interested in volunteering, there’s no better time than now to start your search.
